Artificial Intelligence is not a new word and not a new technology for researchers. This technology is much older than you would imagine. Even there are the myths of Mechanical men in Ancient Greek and Egyptian Myths. Following are some milestones in the history of AI which defines the journey from the AI generation to till date development.
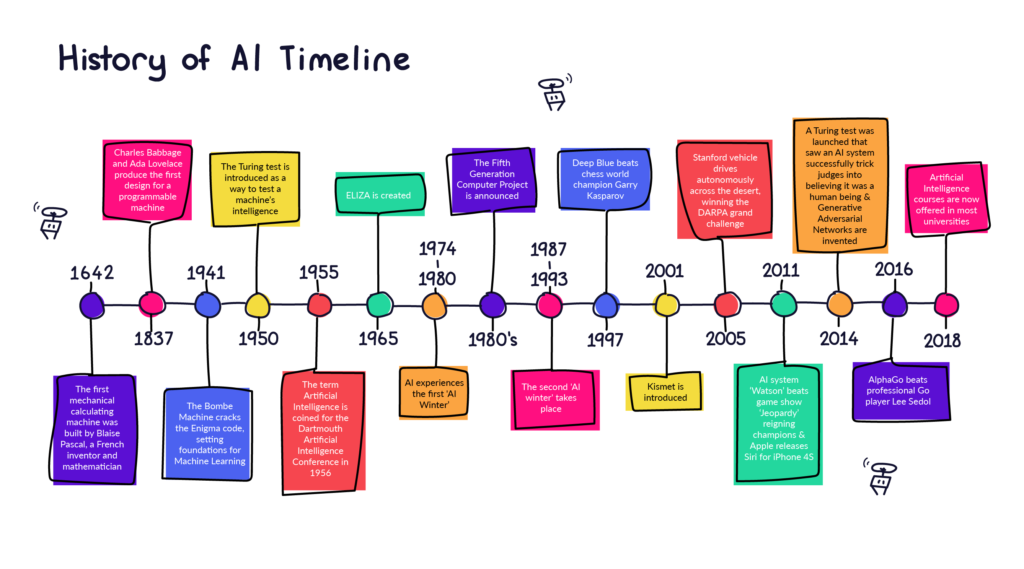
History and Development of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not a novel concept and has roots extending back to ancient myths. Here’s a detailed timeline of significant milestones in AI from its early conceptual stages to its current advancements:
Maturation of Artificial Intelligence (1943-1952)
- 1943: Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts developed the first model of artificial neurons.
- 1949: Donald Hebb introduced Hebbian learning, an updating rule for modifying connection strengths between neurons.
- 1950: Alan Turing published “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” proposing the Turing Test to measure a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to human intelligence.
- 1951: Marvin Minsky and Dean Edmonds created SNARC, the first artificial neural network, using 3,000 vacuum tubes to mimic a network of 40 neurons.
The Birth of Artificial Intelligence (1952-1956)
- 1952: Arthur Samuel developed the Samuel Checkers-Playing Program, the first self-learning program for games.
- 1955: Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon created the Logic Theorist, the first artificial intelligence program, proving 38 of 52 mathematics theorems.
- 1956: John McCarthy coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” at the Dartmouth Conference, marking AI’s establishment as an academic field.
The Golden Years – Early Enthusiasm (1956-1974)
- 1958: Frank Rosenblatt introduced the perceptron, an early neural network capable of learning from data. John McCarthy developed the Lisp programming language.
- 1959: Arthur Samuel coined “machine learning.” Oliver Selfridge published “Pandemonium: A Paradigm for Learning.”
- 1964: Daniel Bobrow created STUDENT, an early program for natural language processing.
- 1965: Edward Feigenbaum, Bruce G. Buchanan, Joshua Lederberg, and Carl Djerassi developed Dendral, the first expert system.
- 1966: Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, the first chatbot. Stanford Research Institute developed Shakey, the first mobile intelligent robot.
- 1968: Terry Winograd developed SHRDLU, a multimodal AI capable of manipulating and reasoning within a world of blocks.
- 1969: Arthur Bryson and Yu-Chi Ho outlined backpropagation for multilayer artificial neural networks. Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert’s book “Perceptrons” highlighted neural network limitations.
- 1972: The first intelligent humanoid robot, WABOT-1, was built in Japan.
- 1973: James Lighthill’s report “Artificial Intelligence: A General Survey” led to reduced government funding for AI research in the UK.
The First AI Winter (1974-1980)
- 1974-1980: Funding for AI research decreased significantly, leading to the first AI winter, characterized by reduced interest and investment in AI.
A Boom of AI (1980-1987)
- 1980: The American Association of Artificial Intelligence held its first national conference. Expert systems like the Lisp machine emerged.
- 1981: Danny Hillis created parallel computers for AI, resembling modern GPUs.
- 1984: Marvin Minsky and Roger Schank warned of an impending “AI winter.”
- 1985: Judea Pearl introduced Bayesian networks for encoding uncertainty in computer systems.
The Second AI Winter (1987-1993)
- 1987-1993: A second AI winter occurred due to high costs and inefficiencies of expert systems, leading to reduced funding and interest.
The Emergence of Intelligent Agents (1993-2011)
- 1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Gary Kasparov. Sepp Hochreiter and Jürgen Schmidhuber introduced Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks.
- 2002: Roomba, the first AI-based home appliance, was introduced.
- 2006: Companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Netflix began using AI.
- 2009: Rajat Raina, Anand Madhavan, and Andrew Ng advocated for using GPUs in deep learning.
- 2011: IBM’s Watson won Jeopardy. Apple launched Siri, a voice-activated personal assistant.
Deep Learning, Big Data, and Artificial General Intelligence (2011-Present)
- 2012: Google launched Google Now. Geoffrey Hinton’s team won the ImageNet challenge with a deep CNN.
- 2013: China’s Tianhe-2 became the fastest supercomputer. DeepMind introduced deep reinforcement learning. Google introduced Word2vec.
- 2014: “Eugene Goostman” passed the Turing Test. Ian Goodfellow introduced GANs. Facebook developed DeepFace.
- 2016: DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated Go champion Lee Sedol. Uber launched a pilot for self-driving cars.
- 2018: IBM’s Project Debater competed in debates. Google Duplex made hairdresser appointments.
- 2021: OpenAI released Dall-E, a multimodal AI system.
- 2022: OpenAI launched ChatGPT, a chat-oriented AI interface.
| Period | Key Events |
|---|---|
| Ancient Concepts | Myths of mechanical men and artificial beings in Greek and Egyptian mythology. |
| 1943-1952 (Maturation) | 1943: McCulloch and Pitts’ artificial neurons. 1949: Hebbian learning. 1950: Turing Test proposed. 1951: Minsky and Edmonds’ SNARC neural network. |
| 1952-1956 (Birth of AI) | 1952: Samuel’s Checkers-Playing Program. 1955: Newell and Simon’s Logic Theorist. 1956: Term “AI” coined by John McCarthy at Dartmouth Conference. |
| 1956-1974 (Golden Years) | 1958: Rosenblatt’s perceptron, McCarthy’s Lisp. 1959: Samuel’s “machine learning.” 1964: Bobrow’s STUDENT NLP. 1965: Dendral expert system. 1966: Weizenbaum’s ELIZA, Shakey robot. 1968: Winograd’s SHRDLU. 1969: Backpropagation and “Perceptrons” by Minsky and Papert. 1972: WABOT-1 humanoid robot. 1973: Lighthill’s report on AI. |
| 1974-1980 (First AI Winter) | Funding and interest in AI declined due to unmet expectations. |
| 1980-1987 (AI Boom) | 1980: First national AI conference. Expert systems resurgence. |
| 1987-1993 (Second AI Winter) | Funding and interest declined again due to high costs and inefficiencies. |
| 1993-2011 (Intelligent Agents) | 1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeats Kasparov. 2002: Roomba vacuum cleaner. 2006: AI in Facebook, Twitter, Netflix. 2009: GPUs in deep learning. 2011: IBM’s Watson wins Jeopardy, Siri launched by Apple. |
| 2011-Present (Deep Learning and Big Data) | 2012: Google Now, deep CNN wins ImageNet. 2013: Tianhe-2, DeepMind’s deep reinforcement learning, Word2vec. 2014: GANs by Goodfellow, DeepFace by Facebook. 2016: AlphaGo defeats Lee Sedol, Uber’s self-driving cars. 2018: IBM’s Project Debater, Google Duplex. 2021: OpenAI’s Dall-E. 2022: OpenAI’s ChatGPT. |
This table provides a concise overview of the key milestones in the history of AI.
Conclusion
AI has significantly evolved from its conceptual stages to advanced applications, driven by deep learning and big data. Companies like Google, Facebook, IBM, and Amazon continue to innovate, promising a future of increasingly intelligent systems.
